What Is Skin Cancer? – Understanding Skin Cancer: Types, Causes, Diagnosis, and Prevention
Introduction
Skin cancer, a menacing and all-too-common threat, casts a shadow over the sunny days we cherish. Our skin, the body’s largest organ, serves as a protective barrier against the elements, making it particularly vulnerable to the sun’s harmful UV rays. Understanding what skin cancer is and its intricacies is not just a matter of medical knowledge; it’s a critical aspect of maintaining our overall health and well-being.
In this article, we embark on a journey to demystify the enigma of skin cancer. We will explore the basics, such as what skin cancer is and the role of the skin in our bodies. This knowledge will empower you to recognize the warning signs and risk factors that should never be ignored. As we delve deeper, we will uncover the various types of skin cancer, from the most prevalent basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas to the more sinister melanoma. By understanding these distinctions, you can be better prepared to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Knowledge is power, and when it comes to skin cancer, it’s a matter of life and death. Join us as we shed light on the causes, types, and prevention of this insidious disease, arming you with the information you need to safeguard your skin and your health.
Types of Skin Cancer
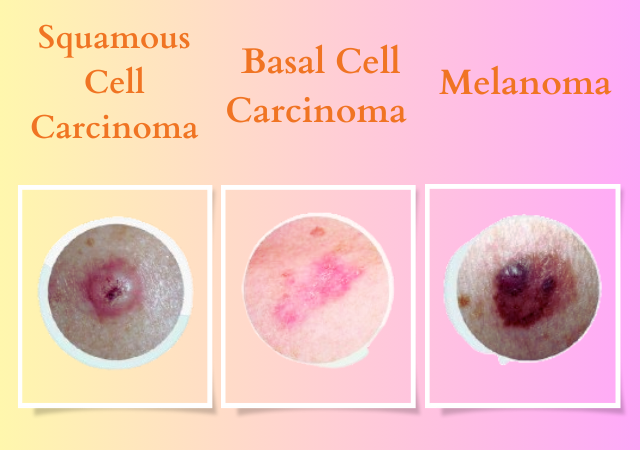
There are several types of skin cancer, with the most common being basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): Basal cell carcinoma is the most prevalent type of skin cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of all cases. This cancer typically develops in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and hands. It tends to grow slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. While BCC is less aggressive than other types of skin cancer, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer, often arising in areas frequently exposed to the sun, like the face, ears, and hands. Unlike basal cell carcinoma, SCC can spread to nearby tissues if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent its advancement and potential disfigurement.
- Melanoma: Melanoma is the most aggressive form of skin cancer and the most likely to metastasize or spread to other parts of the body. Unlike BCC and SCC, melanoma can develop in areas with little sun exposure, including the eyes, genitalia, and the soles of the feet. It often starts as an atypical mole or a new pigmented growth. Melanoma is responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with skin cancer is essential for prevention and early intervention.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds is a primary cause of skin cancer. Prolonged and unprotected sun exposure can damage skin cells and increase the risk of cancer development.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer, as their skin has less natural protection against UV radiation.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer can increase an individual’s susceptibility to the disease.
- Personal History: Those who have previously had skin cancer are at a higher risk of developing it again.
- Age: While skin cancer can affect people of all ages, the risk increases with age.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients, have an elevated risk of skin cancer.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as arsenic, can increase the risk of skin cancer.
Diagnosing Skin Cancer
Early detection of skin cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Dermatologists use various methods to diagnose skin cancer:
- Skin Examination: Dermatologists examine the skin for unusual growths, moles, or changes in existing moles.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious lesion is found, a biopsy is performed. A small tissue sample is taken and analyzed to determine if cancer is present.
- Dermoscopy: Dermoscopy is a non-invasive tool that magnifies the skin’s surface, allowing dermatologists to examine moles and growths in detail.
- Skin Imaging: Techniques like total body photography and confocal microscopy are used for monitoring and early detection in high-risk patients.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for skin cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer. Common treatment methods include:
- Surgery: Surgical excision involves removing the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy tissue. It is a common treatment for basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas.
- Mohs Micrographic Surgery: Mohs surgery is a precise technique used for removing skin cancers layer by layer while sparing healthy tissue. It is often employed for cancers on the face and other delicate areas.
- Radiation Therapy: This therapy utilizes high-energy X-rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It is typically reserved for cases where surgery is not feasible.
- Chemotherapy: In cases of advanced or metastatic skin cancer, chemotherapy may be used to target and kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs stimulate the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is primarily used for advanced melanoma.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs work by blocking specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. They are used for some melanoma cases.
- Palliative Care: In advanced cases where a cure is not possible, palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms, improving quality of life, and providing emotional support.
Prevention and Sun Safety
Prevention is the best defense against skin cancer. Here are some essential sun safety and prevention tips:
- Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Apply it generously and reapply every two hours when outdoors.
- Protective Clothing: Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers your arms and legs.
- Seek Shade: Limit sun exposure during peak hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: UV radiation from tanning beds can be as harmful as natural sunlight. Avoid them entirely.
- Regular Skin Examinations: Perform monthly self-examinations of your skin and visit a dermatologist for annual skin checks.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and healthy.
- Educate Yourself: Be aware of the warning signs of skin cancer and any changes in moles or growths.
Living with Skin Cancer
A skin cancer diagnosis can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that many people successfully overcome the disease. Support resources, such as cancer support groups and counseling, can help individuals and their families cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of a skin cancer diagnosis. Survivor stories and testimonials offer hope and inspiration to those on their journey to recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding skin cancer is paramount for our health and well-being. This article has shed light on the types of skin cancer, emphasizing the prevalence of basal cell carcinoma, the risk of squamous cell carcinoma, and the gravity of melanoma. Knowing the causes and risk factors, from UV radiation exposure to genetic predispositions, equips us with the knowledge needed for prevention and early intervention.
The importance of early diagnosis through methods like skin examinations and biopsies cannot be overstated. Treatment options, tailored to the type and stage of cancer, provide hope for patients. Equally vital are the preventative measures, like sunscreen use, protective clothing, and regular skin examinations.
Remember, a skin cancer diagnosis is not the end but the beginning of a journey. With support, education, and early detection, countless individuals have triumphed over this disease, reminding us that knowledge truly is power when it comes to safeguarding our skin and our lives.

My name is Rohit Vagh and I’m a content writer specializing in fashion and lifestyle. I have three years of experience in this field and have written various articles. My writing style is creative and engaging, and I strive to create content that resonates with my readers. I have a deep passion for fashion and am constantly researching the latest trends and styles to make sure my readers are up to date. I’m excited to continue my career in blogging, and I’m always looking for new opportunities in the fashion and lifestyle space.





